What is Metallography?
Metallography is the scientific study and analysis of the microstructure of metals, alloys, ceramics, and composite materials. Through systematic sample preparation and microscopic examination, it reveals grain boundaries, phases, inclusions, and defects that determine material properties.
Essential for quality control, failure analysis, and materials research across aerospace, automotive, medical devices, energy, and additive manufacturing industries.
The Five-Step Preparation Process
Sectioning
Cut sample to size with minimal damage
Mounting
Embed in resin for handling
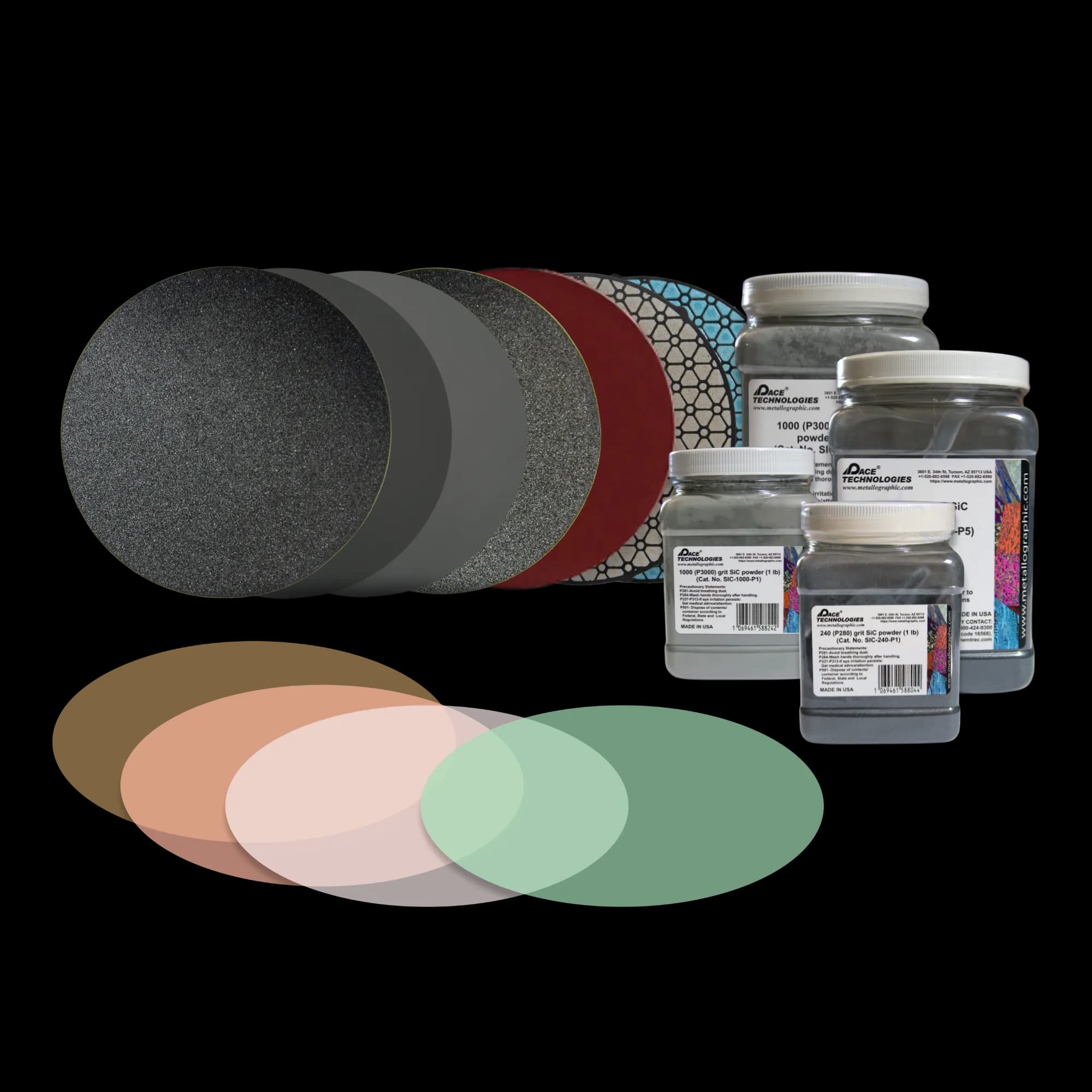
Grinding
Remove damage with progressive abrasives
Polishing
Achieve scratch-free mirror surface
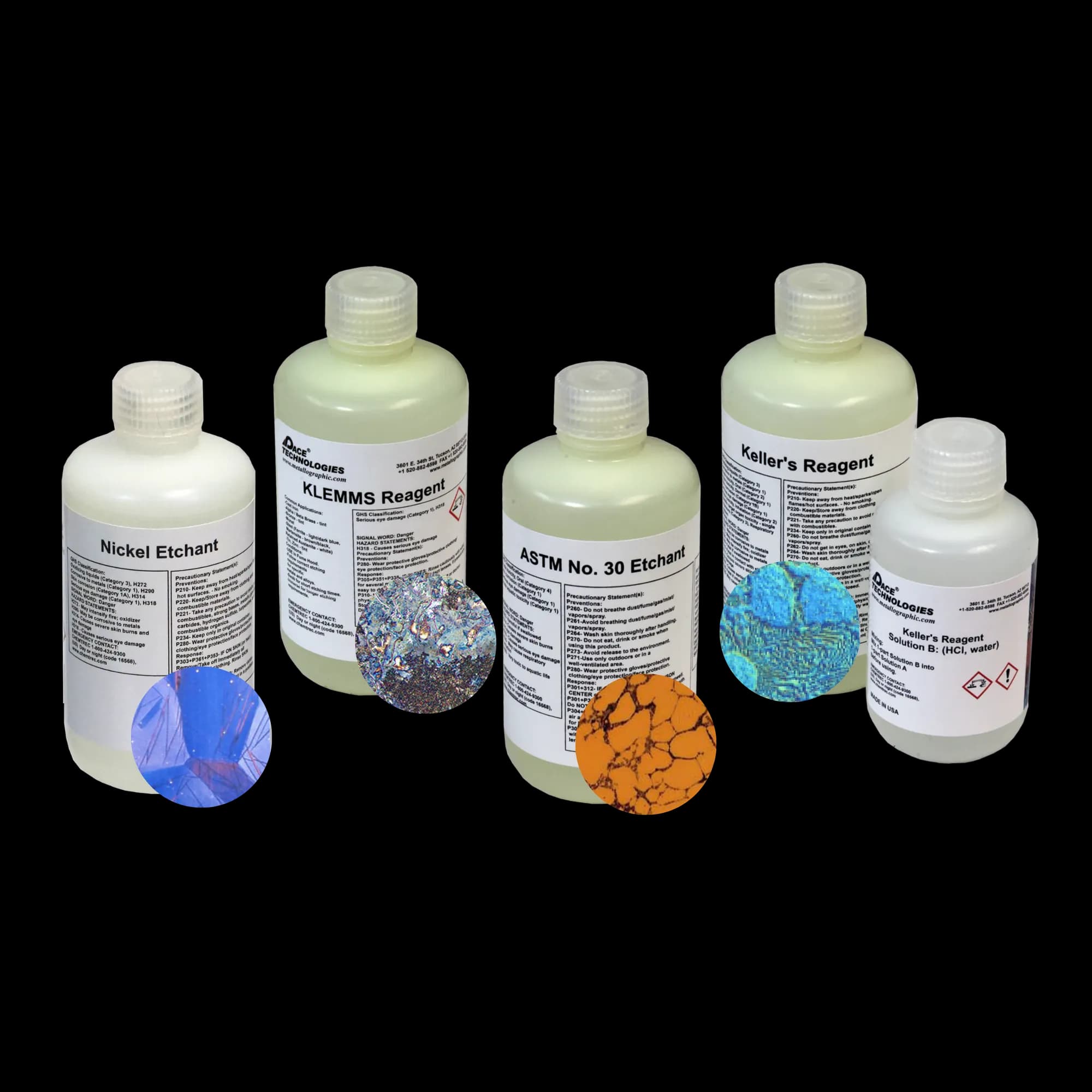
Etching
Reveal microstructure with reagents
Explore our preparation guides, reference tools, ASTM and ISO standards, and reference materials for detailed procedures.